Prerequisites
Database Schema
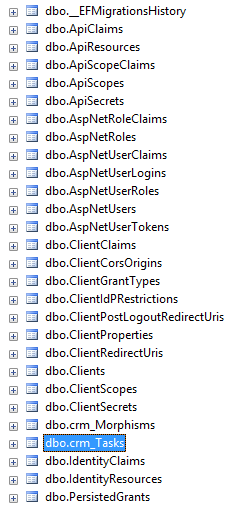
Graph Schema Model
We define the model for columns in database as following
public class ColumnMetadata
{
public string ColumnName { get; set }
public string DataType { get; set; }
}
Then, we do the same thing for the table as below
public class TableMetadata
{
public string TableName { get; set; }
public string AssemblyFullName { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<ColumnMetadata> Columns { get; set; }
}
Because we do the prefix for the table in the database (e.g. dbo.crm_Tasks) so that we need the mapping table that will help us to resolve the friendly name (e.g. tasks when we do the query in UI)
public interface ITableNameLookup
{
bool InsertKeyName(string friendlyName);
string GetFriendlyName(string correctName);
}
public class TableNameLookup : ITableNameLookup
{
private IDictionary<string, string> _lookupTable = new Dictionary<string, string>();
public bool InsertKeyName(string correctName)
{
if(!_lookupTable.ContainsKey(correctName))
{
var friendlyName = CanonicalName(correctName);
_lookupTable.Add(correctName, friendlyName);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public string GetFriendlyName(string correctName)
{
if (!_lookupTable.TryGetValue(correctName, out string value))
throw new Exception($"Could not get {correctName} out of the list.");
return value;
}
private string CanonicalName(string correctName)
{
var index = correctName.LastIndexOf("_");
var result = correctName.Substring(
index + 1,
correctName.Length - index - 1);
return Char.ToLowerInvariant(result[0]) + result.Substring(1);
}
}
Now let put all the schema models into the database metadata as below
public interface IDatabaseMetadata
{
void ReloadMetadata();
IEnumerable<TableMetadata> GetTableMetadatas();
}
public sealed class DatabaseMetadata : IDatabaseMetadata
{
private readonly DbContext _dbContext;
private readonly ITableNameLookup _tableNameLookup;
private string _databaseName;
private IEnumerable<TableMetadata> _tables;
public DatabaseMetadata(DbContext dbContext, ITableNameLookup tableNameLookup)
{
_dbContext = dbContext;
_tableNameLookup = tableNameLookup;
_databaseName = _dbContext.Database.GetDbConnection().Database;
if (_tables == null)
ReloadMetadata();
}
public IEnumerable<TableMetadata> GetTableMetadatas()
{
if (_tables == null)
return new List<TableMetadata>();
return _tables;
}
public void ReloadMetadata()
{
_tables = FetchTableMetaData();
}
private IReadOnlyList<TableMetadata> FetchTableMetaData()
{
var metaTables = new List<TableMetadata>();
foreach (var entityType in _dbContext.Model.GetEntityTypes())
{
var tableName = entityType.Relational().TableName;
metaTables.Add(new TableMetadata
{
TableName = tableName,
AssemblyFullName = entityType.ClrType.FullName,
Columns = GetColumnsMetadata(entityType)
});
_tableNameLookup.InsertKeyName(tableName);
}
return metaTables;
}
private IReadOnlyList<ColumnMetadata> GetColumnsMetadata(IEntityType entityType)
{
var tableColumns = new List<ColumnMetadata>();
foreach (var propertyType in entityType.GetProperties())
{
var relational = propertyType.Relational();
tableColumns.Add(new ColumnMetadata
{
ColumnName = relational.ColumnName,
DataType = relational.ColumnType
});
}
return tableColumns;
}
}
We have the schema models on the codes it will be populated all the schema information of EfCore entities when the application started.
Graph Type
Let now define the type of the GraphQL as below
public class TableType : ObjectGraphType<object>
{
public QueryArguments TableArgs
{
get; set;
}
private IDictionary<string, Type> _databaseTypeToSystemType;
protected IDictionary<string, Type> DatabaseTypeToSystemType
{
get
{
if (_databaseTypeToSystemType == null)
{
_databaseTypeToSystemType = new Dictionary<string, Type> {
{ "uniqueidentifier", typeof(String) },
{ "char", typeof(String) },
{ "nvarchar", typeof(String) },
{ "int", typeof(int) },
{ "decimal", typeof(decimal) },
{ "bit", typeof(bool) }
};
}
return _databaseTypeToSystemType;
}
}
public TableType(TableMetadata tableMetadata)
{
Name = tableMetadata.TableName;
foreach (var tableColumn in tableMetadata.Columns)
{
InitGraphTableColumn(tableColumn);
}
}
private void InitGraphTableColumn(ColumnMetadata columnMetadata)
{
var graphQLType = (ResolveColumnMetaType(columnMetadata.DataType)).GetGraphTypeFromType(true);
var columnField = Field(
graphQLType,
columnMetadata.ColumnName
);
columnField.Resolver = new NameFieldResolver();
FillArgs(columnMetadata.ColumnName);
}
private void FillArgs(string columnName)
{
if (TableArgs == null)
{
TableArgs = new QueryArguments(
new QueryArgument<StringGraphType>()
{
Name = columnName
}
);
}
else
{
TableArgs.Add(new QueryArgument<StringGraphType> { Name = columnName });
}
TableArgs.Add(new QueryArgument<IdGraphType> { Name = "id" });
TableArgs.Add(new QueryArgument<IntGraphType> { Name = "first" });
TableArgs.Add(new QueryArgument<IntGraphType> { Name = "offset" });
}
private Type ResolveColumnMetaType(string dbType)
{
if (DatabaseTypeToSystemType.ContainsKey(dbType))
return DatabaseTypeToSystemType[dbType];
return typeof(String);
}
}
This punch of code above will help the application to identify the data type and some of the query arguments like pagination, projection… See the final part of this article when I show you the result of the query.
Graph Resolver
To make the GraphQL can understand the database schema that we want to populate, then we need to create some of the revolvers as following
public class NameFieldResolver : IFieldResolver
{
public object Resolve(ResolveFieldContext context)
{
var source = context.Source;
if (source == null)
{
return null;
}
var name = Char.ToUpperInvariant(context.FieldAst.Name[0]) + context.FieldAst.Name.Substring(1);
var value = GetPropValue(source, name);
if (value == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException($"Expected to find property {context.FieldAst.Name} on {context.Source.GetType().Name} but it does not exist.");
}
return value;
}
private static object GetPropValue(object src, string propName)
{
return src.GetType().GetProperty(propName).GetValue(src, null);
}
}
And the resolver for each field in the database schema
public class MyFieldResolver : IFieldResolver
{
private TableMetadata _tableMetadata;
private DbContext _dbContext;
public MyFieldResolver(TableMetadata tableMetadata, DbContext dbContext)
{
_tableMetadata = tableMetadata;
_dbContext = dbContext;
}
public object Resolve(ResolveFieldContext context)
{
var queryable = _dbContext.Query(_tableMetadata.AssemblyFullName);
if (context.FieldName.Contains("_list"))
{
var first = context.Arguments["first"] != null ?
context.GetArgument("first", int.MaxValue) :
int.MaxValue;
var offset = context.Arguments["offset"] != null ?
context.GetArgument("offset", 0) :
0;
return queryable
.Skip(offset)
.Take(first)
.ToDynamicList<object>();
}
else
{
var id = context.GetArgument<Guid>("id");
return queryable.FirstOrDefault($"Id == @0", id);
}
}
}
Have you see the dynamic LINQ in the code above (bold text colors). Thank you for System.Linq.Dynamic.Core lib, without it we need to do a lot of more works. And one more thing that makes the query of the assembly name as
public static class DbContextExtensions
{
public static IQueryable Query(this DbContext context, string entityName) =>
context.Query(context.Model.FindEntityType(entityName).ClrType);
static readonly MethodInfo SetMethod = typeof(DbContext).GetMethod(nameof(DbContext.Set));
public static IQueryable Query(this DbContext context, Type entityType) =>
(IQueryable)SetMethod.MakeGenericMethod(entityType).Invoke(context, null);
}
You can reference to https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48041821/dynamically-access-table-in-ef-core-2-0 for the solution.
Graph Query
Now is the time we need to define the query for our application. Two things to notice as following
- If we want to query the entity like { tasks (id: “<id here>”) {id, name} }, then we point it based on the database schema that we have defined so far and the result will only have one record in the output
- But if we want to query the list of entities like { tasks_list (offset:1, first:10) { id, name } } query the list of page 1 and get 10 records, then the result should be a list of records
As you see above, we need to define 2 fields for each entity we have in the database. For example, if you have 10 entities in DbContext, then we have 10 x 2=20 fields in the GraphQL definition. Let me show you a code
public class GraphQLQuery : ObjectGraphType<object>
{
private IDatabaseMetadata _dbMetadata;
private ITableNameLookup _tableNameLookup;
private DbContext _dbContext;
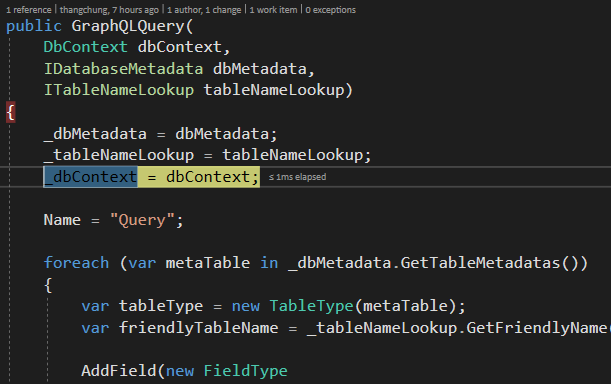
public GraphQLQuery(
DbContext dbContext,
IDatabaseMetadata dbMetadata,
ITableNameLookup tableNameLookup)
{
_dbMetadata = dbMetadata;
_tableNameLookup = tableNameLookup;
_dbContext = dbContext;
Name = "Query";
foreach (var metaTable in _dbMetadata.GetTableMetadatas())
{
var tableType = new TableType(metaTable);
var friendlyTableName = _tableNameLookup.GetFriendlyName(metaTable.TableName);
AddField(new FieldType
{
Name = friendlyTableName,
Type = tableType.GetType(),
ResolvedType = tableType,
Resolver = new MyFieldResolver(metaTable, _dbContext),
Arguments = new QueryArguments(
tableType.TableArgs
)
});
// lets add key to get list of current table
var listType = new ListGraphType(tableType);
AddField(new FieldType
{
Name = $"{friendlyTableName}_list",
Type = listType.GetType(),
ResolvedType = listType,
Resolver = new MyFieldResolver(metaTable, _dbContext),
Arguments = new QueryArguments(
tableType.TableArgs
)
});
}
}
}
We based on the schema that we got from previous steps to define the fields for the GraphQL query. Is it make sense to you so far?
Graph Controller
This final step of this article, we define the controller so that we can run the application. It is really simple as below
[Route("graphql/api/query")]
public class GraphQLController : Controller
{
private readonly Schema graphQLSchema;
public GraphQLController(Schema schema)
{
graphQLSchema = schema;
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<string> Get([FromQuery] string query = "{ tasks_list(offset:1, first:10) { id, name } }")
{
var result = await new DocumentExecuter().ExecuteAsync(
new ExecutionOptions()
{
Schema = graphQLSchema,
Query = query
}
).ConfigureAwait(false);
if (result.Errors?.Count > 0)
{
return result.Errors.ToString();
}
var json = new DocumentWriter(indent: true).Write(result.Data);
return json;
}
}
Don’t forget to wire up all the things to the IOC container as
public static class ServiceCollectionExtensions
{
public static IServiceCollection AddMyGraphQL(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddScoped<ITableNameLookup, TableNameLookup>();
services.AddScoped<IDatabaseMetadata, DatabaseMetadata>();
services.AddScoped((resolver) =>
{
var dbContext = resolver.GetRequiredService<ApplicationDbContext>();
var metaDatabase = resolver.GetRequiredService<IDatabaseMetadata>();
var tableNameLookup = resolver.GetRequiredService<ITableNameLookup>();
var schema = new Schema { Query = new GraphQLQuery(dbContext, metaDatabase, tableNameLookup) };
schema.Initialize();
return schema;
});
return services;
}
}
Put it all together

After finished all the code above, the structure of this as below
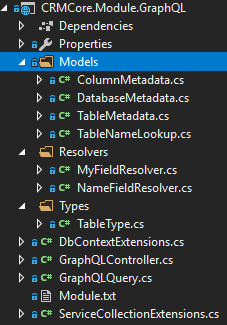
This is just only a POC project so that I will have more refactor in the future. Let run it by press F5, I will show you how it works
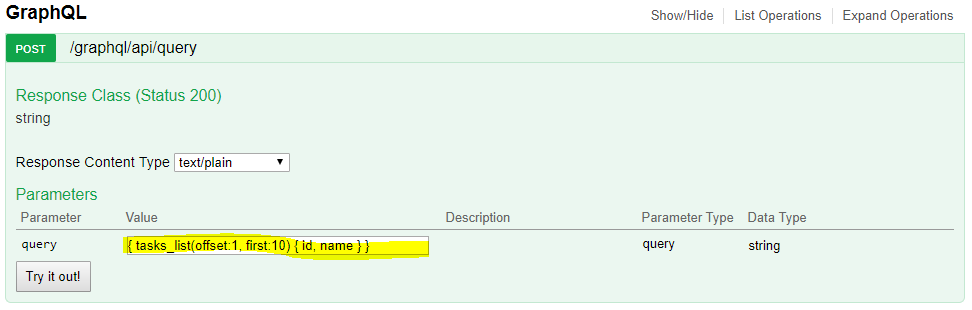
Let input some of GraphQL query above then click Try it out!
The database schema automatically loads as
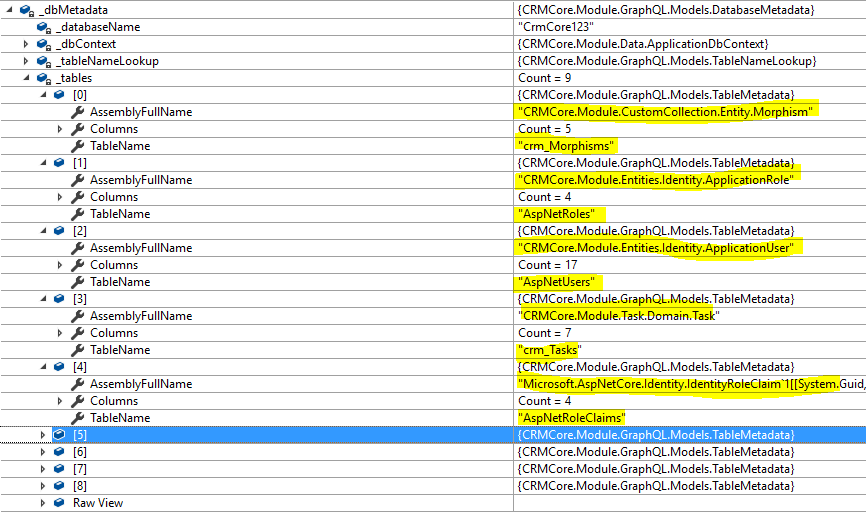
And it builds out all the GraphQL fields as
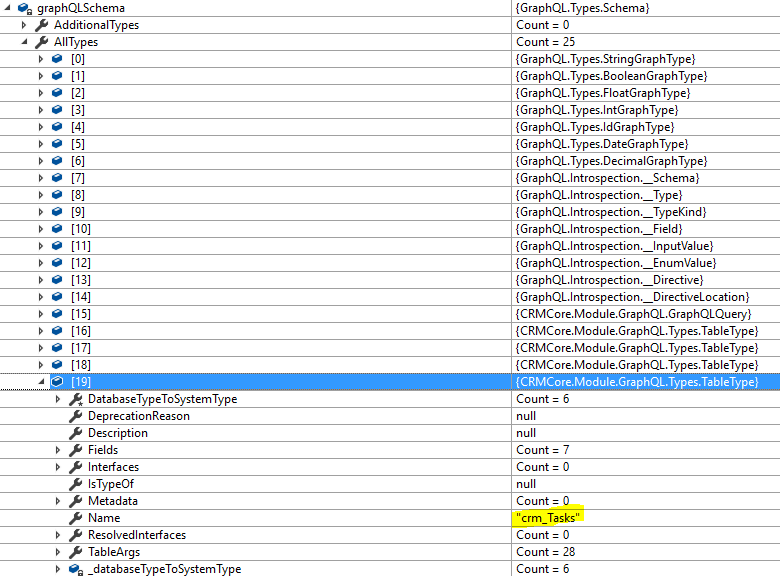
With { tasks_list(offset:1, first:10) { id, name } } for the input, you will receive
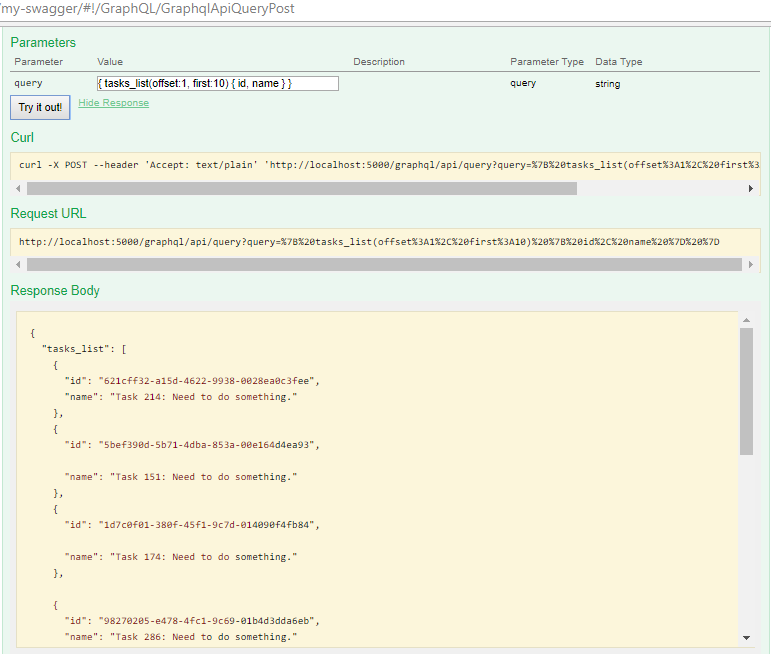
If I change it to { tasks(id: “621CFF32-A15D-4622–9938–0028EA0C3FEE”) { name, id, taskStatus } }, it should be
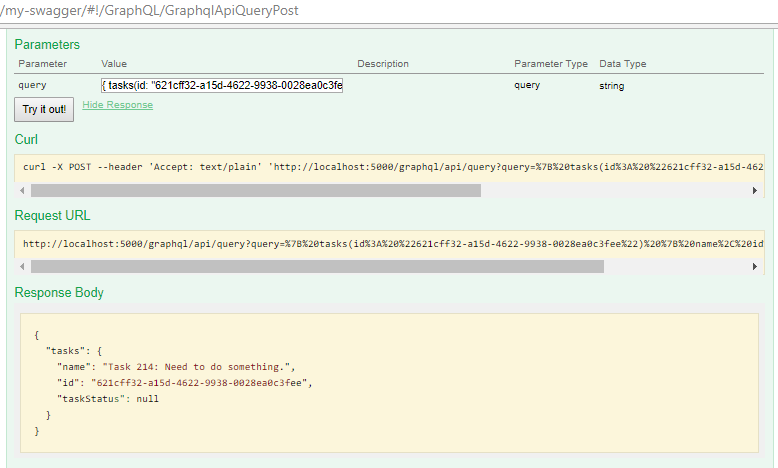
That enough for today  Let me know how do you feel.
Let me know how do you feel.
Source code
All the source code can be found at https://github.com/vietnam-devs/crmcore. If you like it give me a star, then I will have more motivation to it better for the community.
Recap
This article just the POC that I have done for query side. Now you know we can dynamic using some of the libraries in .NET for making the query more dynamic and flexible in the wild world. But some of the caveats I didn’t mention in this article as following
- Authentication and authorization for entities didn’t mention yet.
- Maybe we can hide and don’t expose everything out of the world like this.
- I will continue to work on a mutation side and other concepts of GraphQL in other articles. And also I will integrate with the front-end (react/redux with Apollo client lib) in next time.
- You name it and let me know in the comments then I can improve it later.
Additional Readings
Thanks for reading! If you enjoyed this article, be sure to CLICK 👏 symbol below so OTHERS will SEE it.
The post How to implement Generic Queries by combining EntityFramework Core and GraphQL.NET? appeared first on Crypto Currency Online.
source https://cryptocurrencyonline.co/how-to-implement-generic-queries-by-combining-entityframework-core-and-graphql-net/
No comments:
Post a Comment